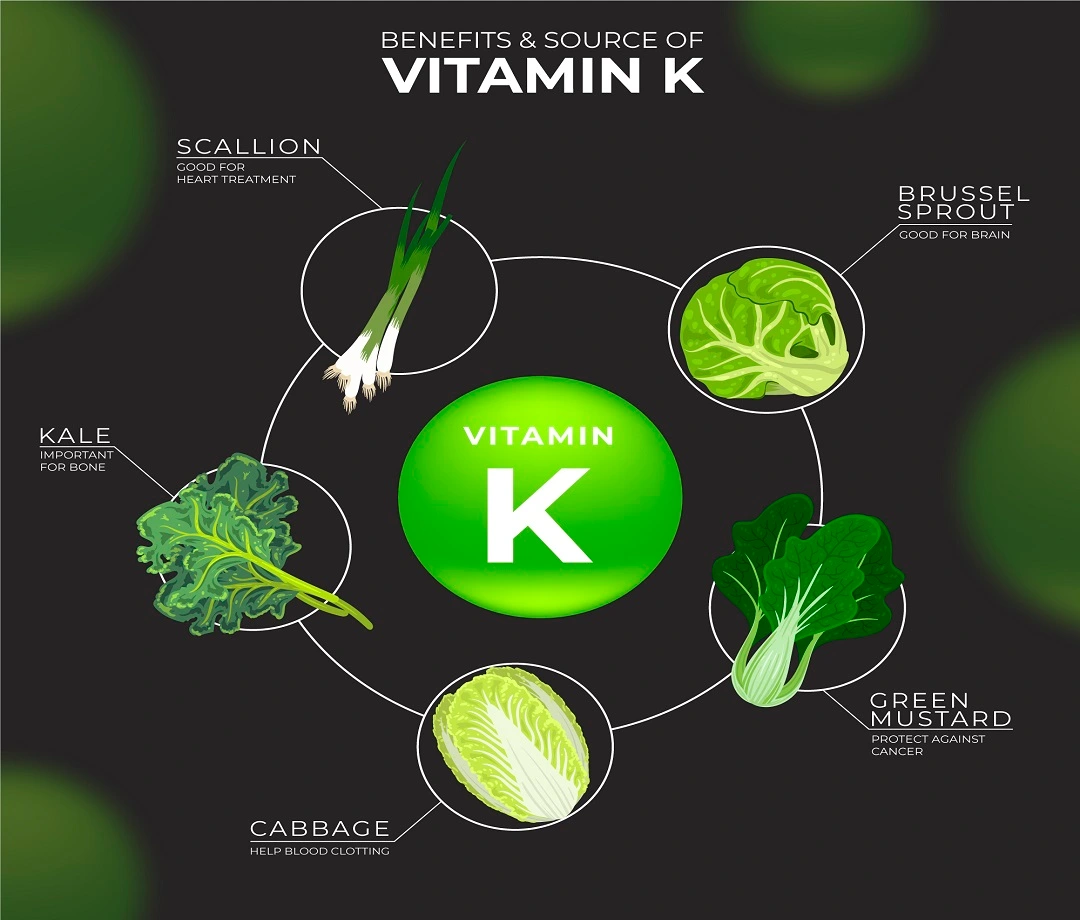
Introduction
Vitamin K is a vital nutrient that often doesn’t get the attention it deserves. While we frequently hear about vitamins like C and D, Vitamin plays crucial roles in our health, particularly in blood clotting and bone health. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the importance of Vitamin, its benefits, food sources, and answer some frequently asked questions to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential nutrient.
What is Vitamin K?
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that comes in two main forms: K1 (phylloquinone) and K2 (menaquinone). Vitamin K1 is primarily found in green leafy vegetables, while Vitamin K2 is present in animal-based and fermented foods. Both forms are essential for different bodily functions.
Benefits of Vitamin K
1. Promotes Blood Clotting
One of the primary roles of Vitamin K is to help in the blood clotting process. Without sufficient Vitamin, your body would be unable to control bleeding when you get a cut or injury. This is because Vitamin activates proteins that are necessary for blood coagulation.
2. Supports Bone Health
Vitamin is crucial for maintaining strong and healthy bones. It helps in the regulation of calcium, ensuring that calcium is deposited in the bones rather than in arteries or soft tissues. This not only promotes bone density but also prevents calcification in the wrong places, which can lead to health complications.
3. Heart Health
By preventing the calcification of arteries, Vitamin plays a significant role in maintaining heart health. This reduces the risk of arterial stiffness, which is a contributing factor to heart disease.
4. Cognitive Health
Emerging research suggests that Vitamin may support brain health and cognitive function. Some studies indicate that it might help in reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
Sources of Vitamin K
To ensure you’re getting enough Vitamin, incorporate the following foods into your diet:
Vitamin K1 Sources:
- Kale
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Lettuce
- Green beans

Vitamin K2 Sources:
- Natto (fermented soybeans)
- Cheese
- Egg yolks
- Liver
- Chicken
- Fermented dairy products
Including a variety of these foods can help you maintain adequate Vitamin levels and enjoy its health benefits.
Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin K varies by age and gender:
- Adult men: 120 micrograms
- Adult women: 90 micrograms
- Children and adolescents: 30-75 micrograms (depending on age)
It’s generally easy to meet these requirements through a balanced diet. However, in some cases, supplements may be necessary, especially for individuals with specific health conditions or dietary restrictions.
FAQ About Vitamin K
Q1: What happens if I don’t get enough Vitamin K?
A deficiency in Vitamin can lead to excessive bleeding, easy bruising, and, over time, reduced bone density and increased risk of fractures. In severe cases, it can cause bleeding in the brain.
Q2: Can I take too much Vitamin K?
Vitamin toxicity is rare, especially from food sources. However, excessive supplementation can interfere with blood-thinning medications. Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking high doses of Vitamin supplements.
Q3: Is Vitamin safe during pregnancy?
Yes, Vitamin is safe and important during pregnancy. It supports proper fetal development and reduces the risk of bleeding in newborns. Pregnant women should aim to meet the recommended dietary intake through food sources.
Q4: How does Vitamin K interact with medications?
Vitamin can interact with anticoagulant medications (blood thinners) such as warfarin. If you’re on such medications, it’s crucial to maintain consistent Vitamin intake and consult with your healthcare provider to avoid complications.
Q5: Are there any conditions that affect Vitamin K absorption?
Certain conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and other gastrointestinal disorders can affect the absorption of Vitamin. Individuals with these conditions should monitor their Vitamin levels closely.
Q6: Can Vitamin improve skin health?
Yes, Vitamin can help improve skin health. It’s often used in skincare products to reduce dark circles, bruising, and spider veins. Its role in blood clotting and tissue repair contributes to these benefits.
Q7: Is Vitamin found in supplements?
Yes, Vitamin is available in supplement form, often combined with other vitamins like D3. This combination is particularly beneficial for bone health.
Q8: What is the difference between Vitamin K1 and K2?
Vitamin K1 is primarily involved in blood clotting, while Vitamin K2 is more effective in promoting bone and heart health. K2 also remains in the body longer and is better absorbed.
Q9: Can I get enough Vitamin from my diet alone?
Most people can get sufficient Vitamin from a well-balanced diet rich in green leafy vegetables, fermented foods, and animal products. However, those with dietary restrictions may need supplements.
Q10: Does cooking affect Vitamin K content in foods?
Yes, cooking can reduce the Vitamin content in foods, especially in vegetables. To preserve Vitamin K, it’s best to consume some of your vegetables raw or lightly steamed.
Vitamin K is an essential nutrient that supports various aspects of health, from blood clotting and bone health to heart and cognitive function. By including a variety of Vitamin rich foods in your diet, you can ensure you’re meeting your daily requirements and reaping the numerous health benefits it offers. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet or starting new supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are on medication.
Incorporate Vitamin into your daily routine and enjoy a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.