Introduction
Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. As one of the eight B vitamins, it is vital for energy production, cell function, and metabolism. In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits of Vitamin B2, its dietary sources, the symptoms of deficiency, and answer some frequently asked questions about this important nutrient.
What is Vitamin B2?
Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, is a water-soluble vitamin that the body needs to break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into energy. It also supports the proper function of the skin, eyes, and nervous system. Since our bodies cannot store Vitamin B2, it is important to consume it regularly through diet.
Benefits of Vitamin B2
Energy Production:
Vitamin B2 is a key player in converting food into energy. It helps in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, ensuring that our bodies have a steady supply of energy.
Antioxidant Properties:
Riboflavin acts as an antioxidant, fighting free radicals that can damage cells and lead to various diseases. This helps in reducing oxidative stress and protecting against chronic conditions.
Healthy Skin and Eyes:
Adequate intake of B2 Vitamin can improve skin health, reducing inflammation and promoting healing. It also supports eye health, potentially reducing the risk of cataracts and other vision problems.
Red Blood Cell Production:
Vitamin B2 plays a crucial role in the production and maintenance of red blood cells, which are essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
Nervous System Support:
This vitamin aids in maintaining the health of the nervous system, ensuring proper nerve function and reducing the risk of neurological disorders.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin B2
Including a variety of foods in your diet can help you meet your daily Vitamin requirements. Some excellent sources of riboflavin include:
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are rich in Vitamin.
- Meat and Fish: Beef, chicken, turkey, and fish like salmon and trout provide good amounts of riboflavin.
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and broccoli are excellent plant-based sources.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds and sunflower seeds are packed with riboflavin.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread can help boost your intake.
- Eggs: Both the yolk and the white contain Vitamin.
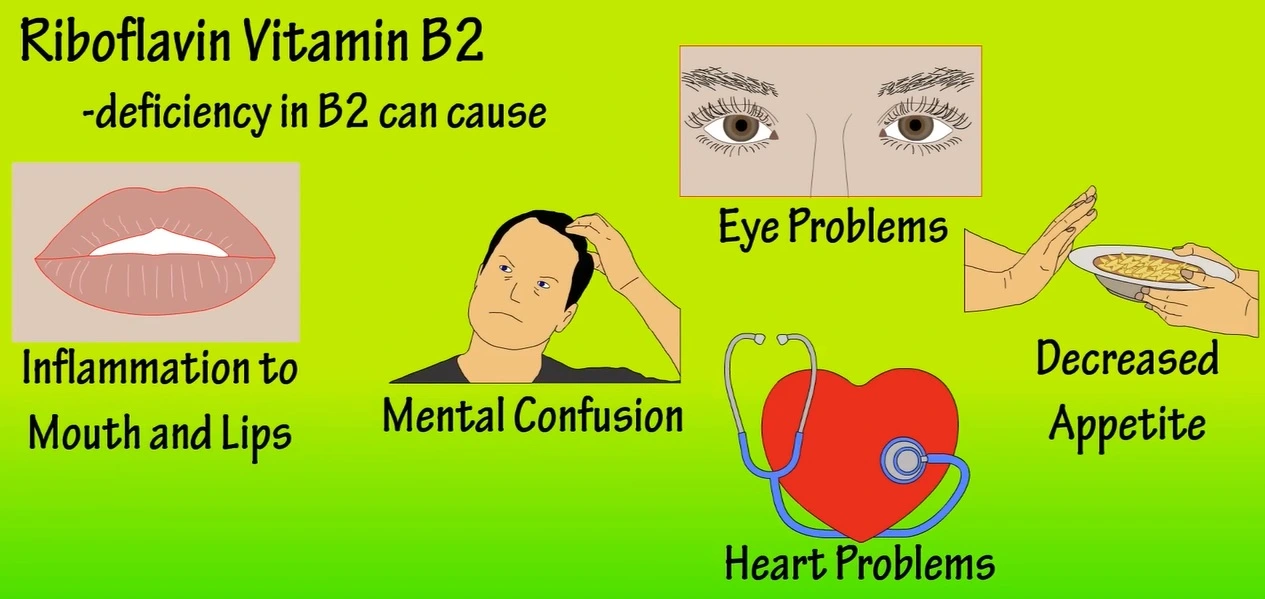
Symptoms of Vitamin B2 Deficiency
A deficiency in B2 Vitamin can lead to a range of health issues. Common symptoms include:
- Skin Disorders: Cracks and sores at the corners of the mouth, dermatitis, and inflamed tongue.
- Eye Problems: Sensitivity to light, itching, burning, and redness of the eyes.
- Fatigue and Weakness: General lack of energy and chronic fatigue.
- Anemia: Reduced red blood cell production can lead to anemia, characterized by weakness and breathlessness.
If you suspect a B2 Vitamin deficiency, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Vitamin B2
Q1. How much Vitamin B2 do I need daily?
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin varies by age, sex, and life stage. For most adults, the recommended amount is approximately 1.3 mg for men and 1.1 mg for women.
Q2. Can I get enough Vitamin B2 from a vegetarian diet?
Yes, vegetarians can obtain sufficient Vitamin from plant-based sources such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fortified cereals.
Q3. Are there any risks associated with too much Vitamin B2?
Vitamin is water-soluble, so excess amounts are usually excreted in urine. However, extremely high doses can cause urine to turn bright yellow and may lead to diarrhea or increased urine output.
Q4. Can Vitamin B2 help with migraines?
Some studies suggest that high doses of riboflavin may reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. Consult your healthcare provider for advice on dosage and suitability.
Q5. Is Vitamin B2 supplementation necessary?
For most people, a balanced diet provides enough B2 Vitamin. However, supplementation may be necessary for individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
Q6. How is Vitamin B2 measured in the body?
Vitamin levels can be assessed through blood tests, which measure riboflavin and its metabolites.
Q7. Does cooking affect Vitamin B2 content in foods?
Riboflavin is sensitive to light but relatively stable when exposed to heat. To preserve its content, store foods away from light and avoid excessive cooking.
Q8. Can Vitamin B2 improve athletic performance?
Riboflavin plays a role in energy production, which is crucial for athletic performance. Adequate intake can help support overall energy levels and endurance.
Q9. Are there any interactions between Vitamin B2 and medications?
Certain medications, such as some antipsychotics and anticonvulsants, can interfere with riboflavin absorption. It’s important to discuss any potential interactions with your healthcare provider.
Q10. What are the signs of a Vitamin B2 overdose?
While riboflavin overdose is rare, symptoms might include itching, numbness, or a burning sensation on the skin. Always follow recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider if you experience adverse effects.
Vitamin B2 is a vital nutrient that supports various bodily functions, from energy production to maintaining healthy skin and eyes. Ensuring you get enough riboflavin through a balanced diet can help prevent deficiency and promote overall well-being. Remember to include a variety of riboflavin-rich foods in your meals, and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns about your Vitamin intake. By understanding the importance of Vitamin, you can take proactive steps towards better health and vitality.

